-
Courses

Courses
Choosing a course is one of the most important decisions you'll ever make! View our courses and see what our students and lecturers have to say about the courses you are interested in at the links below.
-
University Life

University Life
Each year more than 4,000 choose University of Galway as their University of choice. Find out what life at University of Galway is all about here.
-
About University of Galway

About University of Galway
Since 1845, University of Galway has been sharing the highest quality teaching and research with Ireland and the world. Find out what makes our University so special – from our distinguished history to the latest news and campus developments.
-
Colleges & Schools

Colleges & Schools
University of Galway has earned international recognition as a research-led university with a commitment to top quality teaching across a range of key areas of expertise.
-
Research & Innovation

Research & Innovation
University of Galway’s vibrant research community take on some of the most pressing challenges of our times.
-
Business & Industry

Guiding Breakthrough Research at University of Galway
We explore and facilitate commercial opportunities for the research community at University of Galway, as well as facilitating industry partnership.
-
Alumni & Friends

Alumni & Friends
There are 128,000 University of Galway alumni worldwide. Stay connected to your alumni community! Join our social networks and update your details online.
-
Community Engagement

Community Engagement
At University of Galway, we believe that the best learning takes place when you apply what you learn in a real world context. That's why many of our courses include work placements or community projects.
Bio-MINDER
 |
MINDER Minimum Information Model for Dielectric Measurements of Biological Tissues |
|---|
Welcome to Bio-MINDER!
This page describes the Minimum Information Model for Dielectric Measurements of Biological Tissues (MINDER).
The aim of MINDER is to provide a framework for recording and storing dielectric data and metadata for measurements conducted on biological tisues. The minimum information model facilitates the generation of data that is repeatable, interoperable, and re-usable. This page also hosts a database of the results and data obtained using the MINDER.
The data stored and maintained here conforms to the Minimum Information Model for Dielectric Measurements of Biological Tissues (MINDER) structure.
The dielectric properties are inherent characteristics of biological tissues. These quantities, namely, the relative permittivity and conductivity define the interaction of electromagnetic fields with the human body.
Dielectric properties are used in the design and development of electromagnetic medical devices, including diagnostics such as microwave imaging, and therapeutics such as ablation or hyperthermia.
Dielectric properties are typically measured through a straight forward process. However, the properties may vary considerably based on factors such as temperature, tissue state, and probe position. For this reason, it is important to record relevant metadata during the measurement. With the metadata and data combined, dielectric properties of tissues can be interpreted properly and used in a reliable way.
To facilitate this, the MINDER minimum information model has been defined. This structure includes all key types of metadata and enables sharing sharing of data across studies and applications.
The MINDER schema is illustrated below.
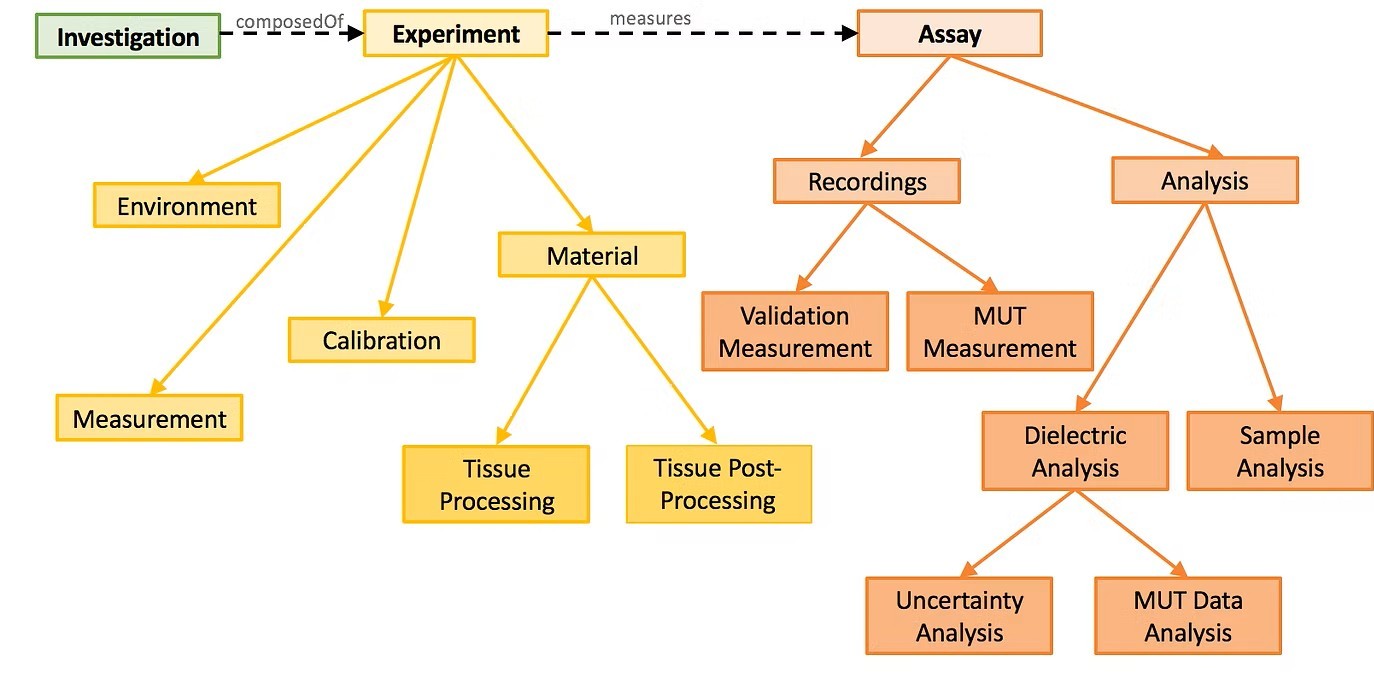
The documentation for the MINDER model is provided here.
Below, find:
- The MINDER specifications (list of all metadata and data; definitions and information)
- Controlled vocabulary
- Data entry template
MINDER Specifications.pdf |
MINDER Controlled Vocabulary.pdf |
Template.xlsx |
MINDER can be cited using:
E. Porter, A. La Gioia, S. Salahuddin, S. Decker, A. Shahzad, M. A. Elahi, M. O'Halloran, and O. Beyan, "Minimum information for dielectric measurements of biological tissues (MINDER): A framework for repeatable and reusable data," International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, Article ID:e21201, 2017.
For any queries or feedback, please contact research team at TMDLab















